BMI Calculator
Your BMI — a ratio of your weight to your height — helps to determine if you are at a healthy weight
Calculate Your Body Mass Index
Your BMI can tell you whether you’re carrying too much, too little or just the right amount of body fat.
En español | Your body mass index (BMI) is an estimate of your body fat that is based on your height and weight. Doctors use BMI, along with other health indicators, to assess an adult’s current health status and potential health risks. People with higher BMIs are more likely to develop chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea and heart disease. To determine your own BMI, use this calculator.
To calculate your BMI, select your height and weight below. When you click the ‘Calculate’ button, you’ll be taken to a section about your results.

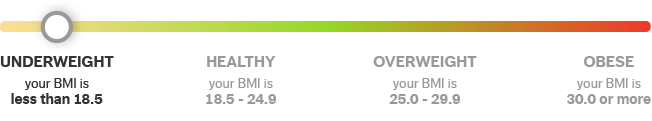
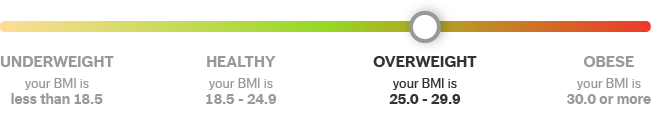
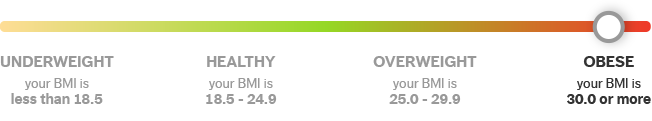
BMI calculator results are grouped into the broad categories: underweight, healthy weight, overweight and obese.
As you review your results, keep in mind that BMI has limitations and that BMI recommendations differ based on gender and other variables. Learn more about how age, race and gender might affect BMI results in our FAQs below.
If you have questions or concerns about your BMI results, talk to your doctor or health care provider. It’s important to know that many factors besides BMI — including family history, eating habits and activity levels — also affect your overall health.
(NOTE: BMI should not be used to assess a child’s weight because the appropriate weight for children varies significantly by age.)
Results
BMI below 18.5
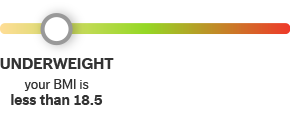
What Your Number Means: Your BMI suggests you are underweight. You may be better able to fight disease and enjoy good health by reaching and maintaining an appropriate weight.
How to Understand Your Results: Keep in mind that BMI has its limits. BMI recommendations differ based on your gender and other variables. And as you age, your muscle tone plays a role. BMI can underestimate body fat in frail, older people who have lost muscle mass. Learn more about how age, race and gender might affect BMI results in our FAQs, below.
Tips for Underweight People Over 50:
- Add more good fats to your meals. Sauté vegetables in olive oil instead of steaming or microwaving them. Add nuts or seeds to stir-fries and oatmeal and avocado to salads, or enjoy a spoonful of peanut butter or other nut butter between meals. These healthy fat sources should help you add pounds without elevating your cholesterol levels.
- Slip healthy liquid calories into your diet. Drink (nonalcoholic) caloric beverages, such as milk or juice, with your meals and/or a nutritional drink like Boost or Ensure between meals.
- Build muscle mass. If your low weight is accompanied by muscle weakness, start a strength training program with resistance bands or small weights. Stronger muscles not only help you perform everyday tasks more easily, but can also add more weight to your frame and fight frailty.
Results
BMI between 18.5 and 24.9

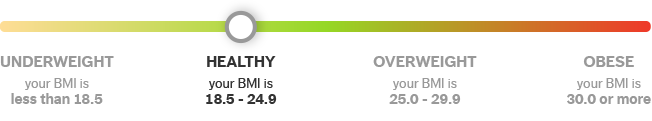
What Your Number Means: Congrats! Your BMI suggests you have a healthy weight. The trick will be to maintain your weight and not gain additional pounds.
How to Understand Your Results: Keep in mind that BMI has its limits. BMI recommendations differ based on your gender and other variables. For instance, your muscle tone plays a role as you age. Learn more about how age, race and gender might affect BMI results in our FAQs, below.
Tips for People Over 50 Who Are a Healthy Weight:
- Anticipate situations that cause weight gain —and have a plan. To maintain a healthy weight, don’t let changing circumstances alter the number on the scale. Sustaining an injury or moving from a job where you’re on your feet all day to one at a desk, for instance, can be a recipe for weight gain. Adjust your calorie intake to account for the activity deficit.
- Weigh yourself once a week. Studies suggest that regular weigh-ins help prevent people from gaining weight. One reason: It’s easier to make an adjustment if you are up by 2 pounds than if you’ve gained 12. In general, people tend to gain one to two pounds per year, which can add up over time.
- Ask about weight gain with new prescriptions. The older you get, the more medications you may take. This can affect your BMI; many drugs list weight gain as a side effect. If you’re prescribed a drug known to put on pounds, ask your doctor for an alternative or suggestions for staying at a healthy weight when no substitute is available.
- Stay active as you age. Some research has shown that physical activity does even more than diet to maintain weight. You can even step it up a notch if you have more time in your schedule.
Results
BMI between 25.0 and 29.9
What Your Number Means: Your BMI suggests you are overweight.
How to Understand Your Results: Keep in mind that BMI has its limits. BMI recommendations differ based on your gender and other variables. For instance, your muscle tone plays a role as you age. Learn more about how age, race and gender might affect BMI results in our FAQs, below.
To get a better read on the health risks associated with your weight, your doctor may combine BMI with a waist circumference measurement called the waist-to-hip ratio. If most of your fat is around your waist, rather than at your hips, you’re at a higher risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes. This risk increases with a waist size that is greater than 35 inches for women or greater than 40 inches for men.
If your BMI falls in the overweight category and you have two or more risk factors for heart disease and related health conditions, losing weight is recommended. Even a weight loss of just 5 to 10 percent of your current weight will help lower your risk of developing diseases. A reasonable and safe rate of weight loss is 1 to 2 pounds per week.
Tips For Overweight People Over 50:
- Start tracking your meals and snacks. One of the secrets of healthy weight loss is to keep a record of everything you eat. Smartphone apps make it easy to do. Tracking can help you see associations you might not have noticed before. With those in mind, you can start to change your behavior and eat less.
- Get moving. Although eating less is key, exercise can be very helpful, especially if it replaces time spent snacking. You’ll see the biggest benefit if you go from being a couch potato to moderately active, but any activity helps while also lowering your risk for chronic diseases.
- Weigh yourself every day. Research suggests that a daily weigh-in helps you to drop pounds. People who weighed themselves every day lost even more weight than those who weighed themselves five times a week. Daily weighing seems to make it easier to adopt weight-loss behaviors.
- Make sure to get a good night’s sleep. People who sleep less than seven hours a night have higher rates of obesity. People on a weight-loss program who slept poorly developed higher BMIs and larger waistlines over a year’s time, research shows. Try turning off digital devices and TVs an hour before bedtime and create a soothing evening ritual to prepare for sleep.
- Ask your doctor about weight-loss medications. There are new drugs as well as combinations of older drugs that have been shown to be effective. You may be a candidate if you have a BMI of 27 to 29, along with another health condition, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Results
BMI 30.0 or above
What Your Number Means: Your BMI suggests that you are obese. A BMI of 40 or more is considered morbidly obese, which carries greater health risks.
How to Understand Your Results: Keep in mind that BMI has its limits. BMI recommendations differ based on your gender and other variables. For instance, your muscle tone plays a role as you age. Learn more about how age, race and gender might affect BMI results in our FAQs, below.
Carrying excess weight puts you at a higher risk for high blood pressure, gallstones, breathing problems and certain cancers.
To get a better read on the health risks associated with your weight, your doctor may combine BMI with a waist circumference measurement called the waist-to-hip ratio. If most of your fat is around your waist, rather than at your hips, you’re at a higher risk for heart disease and type 2 diabetes. This risk increases with a waist size that is greater than 35 inches for women or greater than 40 inches for men.
Weight loss is strongly recommended for people who are obese. Even a weight loss of just 5 to 10 percent of your current weight will help lower your risk of developing diseases. A reasonable and safe rate of weight loss is 1 to 2 pounds per week.
Tips for People Over 50 Who Are Obese:
- Try a prescriptive diet. A balanced diet is generally fine for good health. But if your BMI puts you in the obese category, it can help to follow a proven meal plan, such as a low-fat, low-carb or Mediterranean diet — whatever best matches your lifestyle. Some people have success with intermittent fasting, which involves not eating for certain hours of the day or days of the week. Besides helping you drop excess pounds, it also may improve health conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
- Start moving gradually. If you have been sedentary, ease into activity. Walking, swimming or using a recumbent bicycle or an elliptical machine are easy on the joints and unlikely to lead to injury. As you gain confidence and endurance, you can work out harder. (If you have chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes, check with your doctor first.)
- Avoid or limit processed and ultraprocessed foods. People who eat lots of processed foods (prepared and packaged goods) are heavier than those who eat more whole and unprocessed meals. Instead of breakfast cereal out of a box, eat oatmeal and fresh fruit, for instance. Research shows that when people eat processed foods, the hormones that increase hunger increase and those that suppress appetite decrease.
- Ask your doctor about weight-loss medications or surgery. There are new drugs and combinations of older drugs that have been shown to be effective. You may be a candidate for those if you have a BMI of 30 or more.
- Consider weight-loss surgery. If you have a BMI of 40 or more, ask your doctor about surgical options. If you also have diabetes, you may see an improvement in your condition as well as weight loss afterwards.
FAQs
What is BMI?
BMI, or body mass index, is a screening tool that takes into account a person’s height and weight. It slots people into four weight groups (underweight, healthy weight, overweight, obese) that may be linked to health problems. But BMI doesn’t directly measure a person’s health.
What is a healthy BMI?
The healthy weight category is defined as a BMI of between 18.5 and 24.9. A weight in this category is linked to fewer health problems than the underweight, overweight and obese categories.
What should my BMI be?
The “healthy weight” category—defined as a BMI of between 18.5 to 24.9—is considered ideal. But keep in mind that BMI is not a perfect measure. For example, it does not take into account how much fat you carry or where the fat is distributed, factors that can affect your metabolic health.
How is BMI calculated?
Body mass index (BMI) is a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters.
How accurate is BMI?
That depends. BMI also can’t tell how much of your weight is from fat or muscle, so it misses information important to assessing your health risks.For instance, athletes can have a high BMI because of their muscle mass, even if they’re not overweight. Also, the definitions for the weight categories were based primarily on white populations, so it may be less accurate for people of other races and ethnicities.
How can age or race affect BMI?
BMI doesn’t differentiate between fat, bone and muscle; therefore, it may be less accurate for older people, who tend to lose muscle mass and bone density as they age. (That’s why people over 65 may benefit from a slightly higher BMI, between 25 and 27.) Research shows that the BMI definition of obesity overestimates risk in Black people and underestimates it in individuals of Asian descent, which may lead to inappropriate treatment and health disparities.
Are BMI recommendations the same for men and women?
The recommended amount of body fat differs for men and women. For women, the ideal body fat is 20 to 21 percent. (The average American woman has about 22 to 25 percent body fat.) For men, the recommended amount of body fat is between 13 and 17 percent. (The average American man has about 17 to 19 percent body fat.)
To determine your ideal body weight, try this formula:
- Women: 100 pounds of body weight for the first 5 feet of height + 5 pounds for each additional inch.
- Men: 106 pounds of body weight for the first 5 feet of height + 6 pounds for each additional inch.
If you have a small body frame, however, subtract 10 percent from that number. For a large frame, add 10 percent.
